Scalable End to End ML Data Pipeline using Kafka
Research-Project: Multi-threaded python application capable handling end to end ML workflow from data engineering to predictions
Introduction
Machine Learning (ML) plays a decisive role in converting raw information into useful predictions. For instance, companies like Facebook process millions of photos every day to detect inappropriate contents. This creates a continuous data stream for ML algorithms and systems to face.
ML pipeline is a means of automating the machine learning workflow by enabling data to be transformed and correlated into a model that can then be analyzed to achieve outputs. This type of ML pipeline makes the process of inputting the data into the ML model fully automated.
Here we build a fast scalable machine learning data pipeline with kafka. The training data set used for training the Machine Learning model is stored in the Hadoop file system. Then using batch processing the data is processed and the model is trained.
Data
The dataset that is used for this project is Boston Housing Dataset. Boston Housing dataset is derived from information collected by the U.S. Census Service concerning housing in the area of Boston MA. Link to Dataset.
Technologies, Frameworks, Platforms and Tools
Hadoop
Hadoop is an open source framework that is used to efficiently store and process large datasets ranging in size from gigabytes to petabytes of data. Instead of using one large computer to store and process the data, Hadoop allows clustering multiple computers to analyze massive datasets in parallel more quickly.
Kafka
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed streaming system used for stream processing, real-time data pipelines, and data integration at scale. Originally created to handle real-time data feeds at LinkedIn in 2011.
Architecture
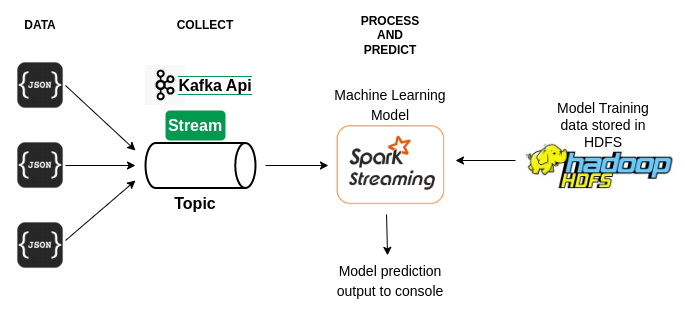
The above block diagram clearly explains the Machine Learning Data pipeline. The Boston housing dataset is stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System. The dataset is then preprocessed and divided into Test and Train dataset. Machine learning Linear Regression model learns from the train dataset and the trained model is then saved. Kafka producer then takes the test dataset and puts randomly picked individual tuples into Kafka message stream. Kafka consumer on the other end picks individual messages from the stream and uses the saved Machine learning pre-trained model to predict the response. The response output is then shown on the console. When a new dataset comes into the Hadoop Distributed file system the kafka producer and consumer halts until the model is trained on the new dataset. As soon as the new model is trained and saved. The consumer and producer resumes with streaming and predictions. The entire application is built in Python programming language and it is multi-threaded.
Implementation
The entire application is built using Python programming language and it is a Multi-threaded python application. There are three primary threads and each of these threads have only one instance and it is implemented using Singleton Design Patterns. The three threads are as follows:
Machine Learning Model Trainer Thread
The machine learning model trainer thread primary task is to train the model and save the trained Linear Regression model. The dataset is read from the CSV file stored in HDFS. The dataset is then split into test and train splits. Linear Regression model is then built using the train split and the model is stored inside the MLmodel folder. Until the model is trained and saved, the Kafka producer thread and Kafka consumer thread are on stand-by and do not proceed with the streaming and predictions.
Kafka Producer Thread
The Kafka producer thread’s primary task is to take the test split of the dataset and send individual randomly picked tuples as messages in the stream in Python dictionary format. The producer is hosted in the localhost at port number 9092. The test split of the dataset is stored in the test_df variable inside the model trainer thread class. Using the instance of the model trainer thread class, the test_df is taken for streaming. Since the Singleton design pattern is used across all the three threads, every thread has access to the variables in every other thread. The main intention of using Singleton design patterns is to create only one instance for a thread class and use it across all the other threads.
Kafka Consumer Thread
The Kafka consumer threads primary task is to consume the messages from the message stream and use the messages for predictions. The consumer thread constantly monitors the model training flags of the ML model trainer thread in loop. When a new dataset is pushed, the thread halts until the training is complete and a new ML model is available for predictions. The flags monitored by the consumer thread are is_model_trained and is_model_available. The auto_offset_reset parameter of the kafka consumer is set to the earliest so that the historical messages are consumed first from the message stream. The retention period of messages in the kafka stream is left with default configuration i.e. 7 days.
Application Running Instructions and Relevant Screenshots
Clone the Git repository, the link is in the Source code section below. Create an EMR M4xlarge instance with spark application and only one master node. Install the kafka software. Scp the application tar file into the master node. Run the bash script setup.sh. This will install all the required library dependencies. Once the dependencies are installed, copy the fs.defaultFS property from core-site.xml in /etc/hadoop/conf/core-site.xml and update the in global parameter HDFS_DATASET_LOC in GlobalConstants.py in the source code directory.
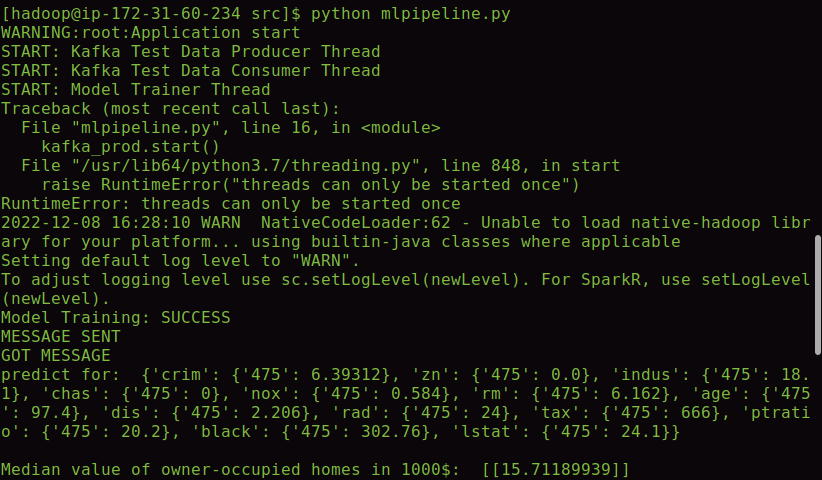
Create a folder called dataset for storing the csv inside HDFS. Create one more directory inside the dataset folder called used to store the datasets which has been already used for training purposes. Now, run the bash script run.sh, this should start the application and the console appears to be as shown in the screenshot below.
Future Work
This application can be further scaled to any extent depending on the requirement and problem statement. However one of the major further developments which can add value to the project is integrating Redis. Least Recently Used (LRU) caching mechanism can be implemented using Redis. LRU cache organizes items in order of use, allowing quick identification of items which have not been used for the longest amount of time.
As the throughput of messages increases, there is a decent probability of getting messages of a particular pattern or identical messages. In such scenarios relying on machine learning model prediction could not be reliable as it may take more time. Hence LRU cache can be used to get super fast predictions for messages with higher appearance count. Also the application can also be designed using FLASK framework, where we can use cron jobs to train machine learning models and REST API’s to push messages to kafka stream and document predictions.
